In today’s fast-paced technological era, the boundaries between humans and machines are steadily fading. The rise of Artificial Intelligence, automation, and advanced computing has created an entirely new space of collaboration known as Human Machine Interaction (HMI). This field explores how people and machines communicate, understand each other, and work together to achieve shared goals.
From simple touch interfaces on our smartphones to complex industrial systems powered by intelligent agents, HMI defines how comfortably and effectively humans engage with technology. The true magic happens when the interaction feels natural, intuitive, and efficient.
At BigAIAgent.tech, our focus is to highlight the growing importance of intelligent systems that understand humans not just as users, but as partners in innovation. The Human Machine Interaction portfolio captures this philosophy by showing how humans and machines can achieve more when they truly connect.
Understanding Human Machine Interaction
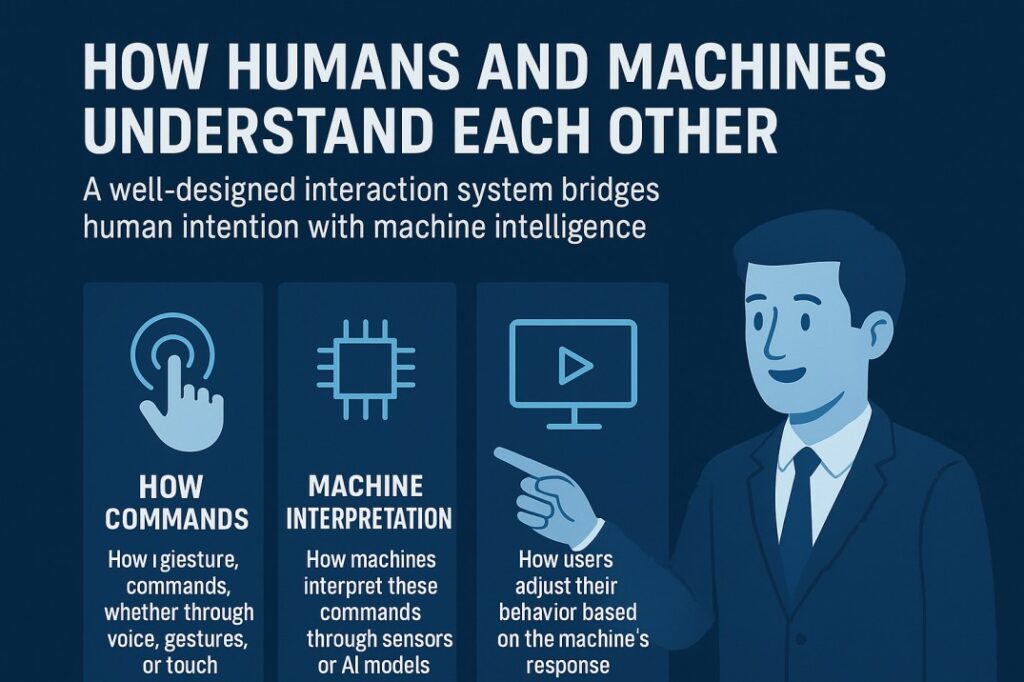
Human Machine Interaction, often abbreviated as HMI, refers to the design and study of systems that allow humans to communicate with machines. This includes everything from voice assistants, robotics interfaces, and AI dashboards to augmented reality systems and autonomous devices.
A well-designed interaction system ensures that both the human and the machine can understand each other easily. It covers:
- How humans send commands, whether through voice, gestures, or touch
- How machines interpret these commands through sensors or AI models
- How machines provide responses, feedback, or visual cues
- How users adjust their behavior based on the machine’s response
In simple terms, HMI bridges human intention with machine intelligence. The more seamless the bridge, the better the experience.
Why Human Machine Interaction Matters
The way humans interact with machines defines how well technology can serve real-world needs. A well-crafted HMI leads to higher efficiency, improved safety, and a stronger sense of trust between people and intelligent systems.
- Enhancing User Experience (UX):
When machines respond smoothly to user actions, the interaction feels effortless. This reduces user frustration and increases satisfaction. Whether it is a factory operator controlling heavy machinery or a user setting preferences on a smart home device, a good HMI design ensures comfort and ease. - Building Safety and Trust:
Machines must behave predictably and transparently. Clear feedback loops, such as visual or auditory signals, help users feel confident that their commands are being understood correctly. This trust is essential in autonomous systems like self-driving vehicles, drones, and robotic assistants. - Encouraging Adoption and Engagement:
People are more likely to use technology that feels natural. A system that understands voice, emotion, or gesture is far more engaging than one that requires technical expertise. - Driving Innovation:
HMI sits at the crossroads of AI, cognitive science, and human psychology. It allows engineers, designers, and researchers to innovate by combining empathy and intelligence in system design.
Key Components of Human Machine Interaction
To truly understand HMI, one must explore its fundamental components. Each plays a vital role in shaping how machines and humans connect.
- Input: The way users communicate with machines (for example, through gestures, voice commands, eye tracking, or touch).
- Processing: The machine’s interpretation of user input using AI models, algorithms, or decision-making frameworks.
- Output: The way the system responds, which could include visuals, sounds, or physical movements.
- Feedback: The loop that ensures users understand the system’s response and adjust their behavior accordingly.
The best HMI systems constantly learn and adapt. They evolve based on user data, improving their ability to predict human intent over time.
The Power of Design Thinking in HMI
A successful human machine interface is not just a product of programming. It is the result of careful design thinking, an approach that prioritizes human needs, emotions, and experiences.
When creating HMI systems, designers consider several questions:
- What is the user trying to achieve?
- How much cognitive effort does the system require?
- Does the interface feel intuitive and enjoyable to use?
- Are users able to recover easily from errors?
Designing for humans means making complex technologies simple, elegant, and useful. The ultimate goal is to make the machine feel like an intelligent assistant rather than a cold system of buttons and commands.
Real World Examples of Human Machine Interaction
- Voice Assistants:
Devices like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant rely heavily on HMI. They use natural language processing to interpret voice commands and provide relevant responses, creating a conversational experience between humans and machines. - Smart Cars and Autonomous Vehicles:
Modern vehicles now use HMI to improve safety and driving comfort. Features such as voice navigation, adaptive cruise control, and driver monitoring systems show how machines can sense, interpret, and react to human behavior. - Industrial Automation:
In factories, operators interact with robots through intuitive dashboards, wearable devices, or gesture-based controls. These systems ensure precision while reducing the risk of human error. - Healthcare and Assistive Technologies:
From robotic surgery systems to AI-powered diagnostic tools, healthcare technology depends on effective HMI to assist doctors and improve patient outcomes. - Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR and VR):
AR and VR experiences rely on motion sensors and visual tracking to create immersive environments where humans interact naturally with virtual elements.
What Makes a Great HMI Project for a Portfolio
If you are building or showcasing a Human Machine Interaction project, it is important to highlight both the technical and human aspects. Here is how you can structure it:
- The Objective:
Explain the challenge or problem you set out to solve. For example, you might aim to improve the accuracy of gesture recognition or make an industrial control interface safer. - The Approach:
Describe how you combined hardware, AI, and user design principles to create an interactive system. - Technology Stack:
List the tools, sensors, and frameworks you used. This could include machine learning algorithms, data pipelines, or UX frameworks. - Interaction Flow:
Walk through the process of user input, machine processing, and feedback. - Challenges and Solutions:
Discuss what problems you faced, such as inaccurate sensor readings or latency issues, and how you resolved them. - Outcomes and Learnings:
Share measurable results. For example, “User satisfaction increased by 30 percent after interface redesign.” - Future Directions:
Mention how your system could evolve with advancements in AI, sensors, or user research.
By presenting your project with a blend of storytelling, data, and design rationale, you demonstrate both technical skill and empathy, two essential qualities in today’s AI-driven world.
The Future of Human Machine Interaction
The coming years will see an even deeper integration between human intuition and machine intelligence. As AI becomes more capable, machines will not just execute commands but anticipate needs, understand emotions, and act with contextual awareness.
Some of the trends shaping the future of HMI include:
- Emotion-Aware Systems: Machines that detect and respond to human emotions through facial recognition and voice tone analysis.
- Multimodal Interfaces: Combining voice, vision, and touch for more natural interaction.
- Personalization Through AI: Systems that adapt their interface and behavior based on user preferences and habits.
- Haptic Feedback: Advanced sensory feedback that allows users to feel digital interactions.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Robots designed to work safely and intelligently alongside humans in shared environments.
The ultimate goal is to create systems that are not just intelligent but also empathetic, machines that understand context, respect boundaries, and enhance human creativity instead of replacing it.
Conclusion
Human Machine Interaction is no longer a futuristic idea; it is the present reality of how technology evolves with us. Whether it is a smart assistant at home, a robot in a factory, or an AI-driven marketing tool, HMI defines how comfortably humans and machines coexist.
For innovators, designers, and businesses alike, understanding HMI means understanding the language of the future. It is about creating systems that make technology feel human, approachable, responsive, and adaptive.
Halloween Wishes from BigAIAgent.tech
As the lights dim and the world celebrates the season of creativity and mystery, let us remember that technology too has its share of magic. Just as a good Halloween story brings imagination to life, a powerful human machine interaction brings intelligence to life.
Here’s wishing everyone a spooktacular Halloween filled with innovation, imagination, and intelligent connections. May your projects be full of bright ideas, your data clean, and your code bug-free.
Happy Halloween from the BigAIAgent.tech family!