AI is evolving fast, but progress isn’t about chasing hype. It’s about creating systems that work seamlessly, think contextually, and scale reliably.
At BigAIAgent.tech, we’re exploring what happens when intelligence moves from conversation to capability, when AI stops just answering and starts acting.
That’s the promise of AI Agents, autonomous systems designed not just to assist, but to analyze, decide, and deliver outcomes.
We stand at a turning point where AI is transitioning from an information tool to an operational partner.
Let’s explore how we got here, where it’s headed, and what it means for the future of business, technology, and human collaboration.
1. The Rise of AI Agents: From Queries to Actions
When ChatGPT launched in late 2022, it marked a new chapter in how humans interact with machines. For the first time, millions could converse naturally with an AI that understood context and generated coherent, often impressive responses.
But as the technology matured, a deeper question emerged: What if AI could do more than talk?
That question gave birth to the idea of AI agents, systems that can take instruction, plan steps, and perform tasks across digital environments.
Unlike static chatbots, agents are goal-oriented.
They:
- Understand objectives, not just commands.
- Break problems into logical steps.
- Execute actions autonomously across tools and APIs.
- Learn and adapt from feedback.
An AI agent doesn’t just tell you what to do. It actually does it.
Whether that means preparing reports, conducting research, writing code, managing workflows, or even browsing the web, the focus is clear: turn intelligence into execution.
2. Why 2025 Marks the Agentic Shift
2025 is being called the Year of the AI Agent, and not without reason.
The technology landscape has evolved from text generation to task automation — and it’s reshaping how we work.
a. ChatGPT Atlas and the AI-Native Browser
OpenAI’s new ChatGPT Atlas browser is a prime example. Instead of treating AI as a separate tool, Atlas embeds intelligence directly into your browsing experience.
The assistant can read pages, extract insights, compare data, summarize research, and even complete tasks, all from the same window.
Atlas transforms the browser from a passive viewing tool into an interactive workspace, powered by your personal AI. It’s not just search and scroll anymore, it’s understand and act.
b. Agentic Platforms Everywhere
Across the ecosystem, every major AI player is building toward autonomy:
- Google’s Gemini 2.0 integrates agentic workflows into productivity tools.
- Anthropic’s Claude emphasizes reasoning and memory for sustained task completion.
- Meta’s Llama 3.2 focuses on embedded AI that understands user behavior across apps.
- Independent projects like AutoGPT, CrewAI, and Devin (the “AI software engineer”) show agents that can plan, code, and iterate, almost like junior developers.
c. From Experimentation to Execution
What was once experimental, agents that could browse, fetch data, and make decisions — is now entering production.
Businesses are embedding AI into every layer of their workflow, from customer interactions to internal analytics.
This is no longer the “prompt and reply” era.
It’s the plan and perform era.
3. The Architecture of an AI Agent
To understand the power of AI agents, it helps to know how they work behind the scenes.
A robust agent typically combines four key components:
- Reasoning Engine: This is the core intelligence — the large language model (LLM) that interprets instructions, plans actions, and handles logic.
- Memory System: Agents remember context, previous actions, and outcomes. This makes them adaptive and consistent across sessions.
- Toolset Integration: APIs, browsers, data systems, and applications that the agent can control.
- Feedback Loop: The mechanism through which the agent learns from results and optimizes performance.
This architecture enables agents to function like digital teammates, taking initiative, maintaining continuity, and delivering results without micromanagement.
4. The New Foundation: Context, Data, and Trust
As AI agents become more autonomous, the success of their deployment depends on three foundational pillars.
a. Data Quality
Agents need clean, structured, and up-to-date data to make sound decisions.
Without it, even the smartest models can go wrong.
Enterprises investing in AI agents are increasingly focusing on data pipelines, governance, and metadata accuracy, because autonomy without accuracy is chaos.
b. Context Awareness
True intelligence is contextual.
An agent must understand not just what a task is, but why it matters, who it affects, and where it fits in the bigger picture.
Our development philosophy centers on contextual intelligence, teaching agents to comprehend business goals, user preferences, and system environments.
c. Trust and Governance
The more capable agents become, the higher the stakes.
Businesses must ensure that every action, from data access to decision-making, is auditable, ethical, and compliant.
Responsible AI isn’t a checkbox; it’s a design principle.
That’s why we emphasize security, explainability, and user control in every deployment.
5. From Hype to Real Impact: Business Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are rapidly moving from labs to boardrooms, changing how organizations operate. Here’s how they’re being used across key domains:
1. Enterprise Workflows
AI agents are automating time-consuming processes, preparing reports, analyzing metrics, updating records, and scheduling tasks.
They act as workflow assistants that integrate directly into tools like Slack, Notion, or Salesforce, reducing manual effort by up to 60%.
2. Customer Engagement
Instead of rigid chatbots, companies now deploy customer experience agents that understand tone, history, and intent.
They can handle complex service requests, recommend solutions, and escalate only when needed, creating smoother, more human-like interactions.
3. Marketing and Sales
From campaign analytics to personalized outreach, agents analyze customer data, identify leads, and even draft communications tailored to audience behavior.
Sales teams use them to manage pipelines, qualify prospects, and automate routine follow-ups.
4. Product Development
In software development, agentic systems can write code snippets, run tests, debug errors, and suggest optimizations.
Devin, the “AI engineer,” is just one example of how agents are augmenting developers’ productivity.
5. Decision Support
C-suite leaders use agents as real-time analysts, pulling insights from diverse datasets, simulating outcomes, and visualizing impact.
These agents don’t replace decision-makers; they equip them with clarity.
6. Operations and Compliance
In regulated sectors like healthcare and finance, agents monitor workflows, track compliance, and generate audit-ready reports automatically, turning reactive oversight into proactive assurance.
The takeaway is clear: AI agents are no longer a luxury, they’re a necessity for efficiency and scale.
6. The Future Landscape: Where AI Agents Are Headed
The journey of AI agents is only beginning. Over the next decade, we’ll see several key shifts redefining the landscape.
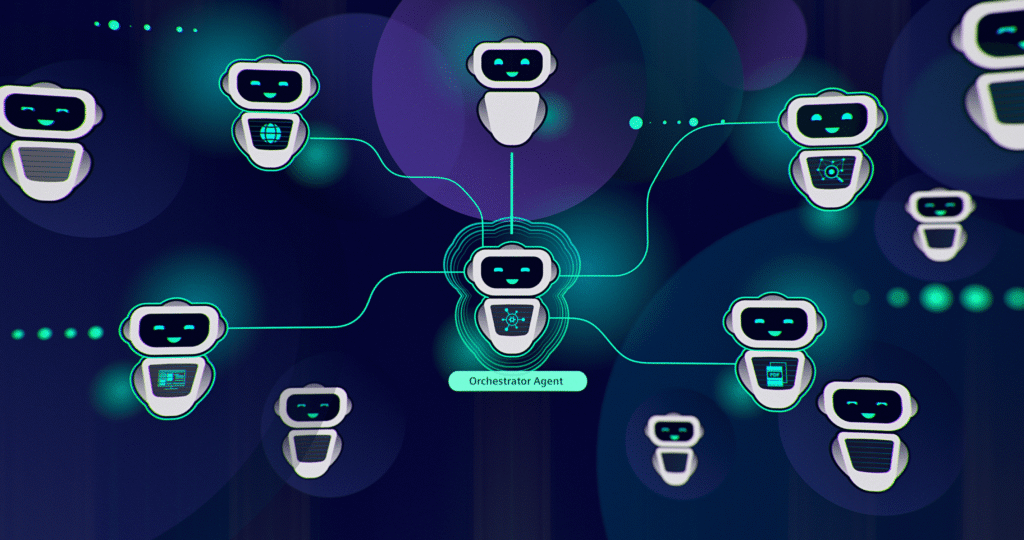
a. Multi-Agent Collaboration
The next leap isn’t a single all-knowing AI, it’s ecosystems of specialized agents collaborating on complex tasks.
Imagine a marketing agent coordinating with a data analyst agent, both overseen by a project-manager agent, completing multi-step projects seamlessly.
b. Embedded Intelligence Everywhere
With AI-native browsers like ChatGPT Atlas and AI-integrated OS platforms on the horizon, every digital environment will have built-in intelligence.
Workflows will happen in natural language, not drop-down menus.
c. Physical and IoT Integration
As robotics advances, AI agents will move from screens into the physical world, managing warehouses, logistics, and even medical devices.
The boundary between digital and physical intelligence will blur.
d. Continual and Personalized Learning
Tomorrow’s agents won’t reset after each interaction. They’ll remember preferences, learn behavior patterns, and continuously improve performance, securely and ethically.
e. AI Regulation and Human Oversight
Governments and organizations are creating frameworks to ensure accountability, transparency, and user control.
Expect a world where AI agents operate under digital “licenses,” ensuring safety and governance.
7. Human + AI Collaboration: The True Vision
The rise of AI agents isn’t about replacement, it’s about augmentation.
Humans bring intuition, empathy, and creativity; agents bring consistency, speed, and scale.
The future workplace will be hybrid, humans setting vision, AI executing precision.
Consider these transformations:
- Analysts freed from manual data pulls, focusing instead on interpretation.
- Writers assisted by research agents that compile context.
- Product managers supported by agents tracking feature adoption in real time.
- Developers collaborating with AI pair programmers.
The goal isn’t to automate people, it’s to elevate their impact.
8. How We Are Building What Works
Here, our mission is simple yet powerful:
To create AI agents that make intelligence practical, not theoretical.
We focus on four pillars:
1. Purpose-Built Design
Every agent we build starts with a clear purpose, not a general model trying to do everything.
Our approach ensures efficiency, reliability, and measurable outcomes.
2. Seamless Integration
We embed agents directly into existing business ecosystems, CRMs, ERPs, analytics dashboards, or custom APIs.
The result: minimal friction, maximum adoption.
3. Secure and Ethical Frameworks
From data encryption to permissioned memory, our agents are built for compliance-driven environments.
We prioritize transparency, auditability, and privacy.
4. Scalable Infrastructure
Our systems are designed to move from pilot to production effortlessly.
Whether for startups or enterprises, we ensure that scaling AI doesn’t mean losing control.
Because the future of AI isn’t about flashy demos.
It’s about building what truly works, at scale, with trust.
9. Challenges on the Road Ahead
Like any transformative technology, AI agents come with their share of challenges.
- Interpretability: Ensuring we can explain why an agent took a certain action.
- Over-Automation Risks: Maintaining the right balance between autonomy and oversight.
- Ethical Bias: Preventing agents from perpetuating or amplifying human biases.
- Data Fragmentation: Integrating data from multiple systems securely and coherently.
- Change Management: Helping organizations and teams adapt to agent-driven workflows.
10. Looking Ahead: The Agentic Decade
The next decade will belong to agentic AI, systems that plan, act, and evolve.
We’ll see AI become the operating layer of work, not just an add-on.
Organizations that embrace agents early will gain compounding advantages — faster innovation, lower costs, and deeper intelligence.
And just as the internet once redefined access to information, AI agents will redefine access to capability.
Beyond Hype, Toward Utility
AI agents are more than the next tech trend, they’re a rethinking of how work gets done.
They mark the shift from interaction to execution, from reactive systems to proactive intelligence. To make intelligence actionable, ethical, and endlessly scalable.
Because in the end, the future of AI isn’t about replacing humans.
It’s about empowering them, with systems that think, learn, and work alongside us.