Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as one of the most transformative forces in human history, reshaping industries, economies, and everyday life. Beyond automation and data analysis, one of AI’s most inspiring impacts lies in the fact that now we can easily get the knowledge of AI in empowering persons with disabilities. From improving communication and mobility to enabling inclusion in education and the workplace, AI is creating a world that is more accessible, equitable, and human-centered.
The Accessibility Revolution: Where AI Meets Inclusion
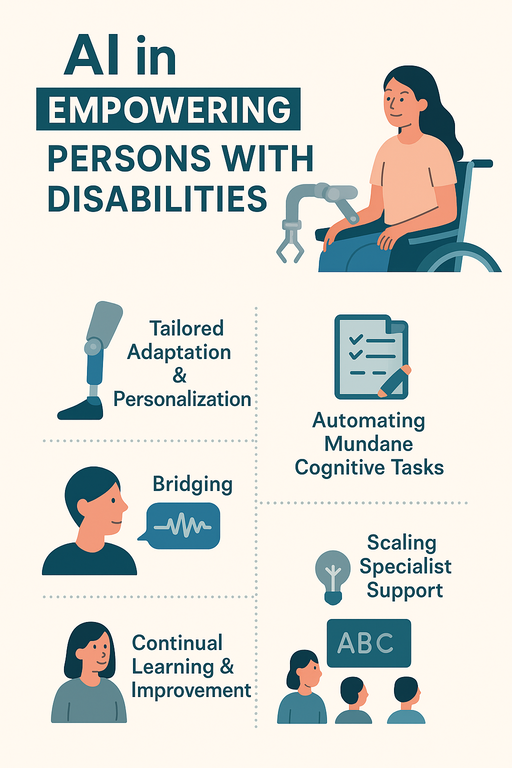
Accessibility has long been a challenge for individuals with physical, cognitive, or sensory disabilities. Traditional tools often addressed only specific needs, leaving significant gaps in independence and participation. AI has changed this narrative by making technology more adaptive, personalized, and context-aware.
AI-driven solutions are now capable of recognizing speech, images, gestures, and even emotions, helping bridge communication barriers and giving people new ways to interact with the digital and physical world. With AI, accessibility is no longer an afterthought, it is becoming an integral part of design and development across industries.
Enhancing Communication Through AI
For people with speech or hearing impairments, AI-powered communication tools are life-changing. Speech-to-text applications like Google Live Transcribe or Microsoft’s AI Captioning convert spoken words into real-time text, allowing seamless communication in classrooms, offices, and public spaces.
Similarly, natural language processing (NLP) models are helping those with non-verbal communication needs by converting typed or gesture-based input into spoken language. Virtual assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant have become more intuitive, enabling users with mobility challenges to perform tasks through simple voice commands.
AI sign language translators are another breakthrough, using computer vision to interpret sign gestures and translate them into spoken or written text. These innovations are not only practical tools but also bridges of empathy, ensuring everyone can express themselves and be understood.
AI for Visual and Hearing Assistance
For individuals with visual impairments, AI-driven applications like Seeing AI and Be My Eyes are revolutionizing everyday life. These tools use image recognition and computer vision to describe surroundings, identify objects, and read printed text aloud. They can even detect facial expressions and help users recognize people in real time.
In the same way, AI in empowering persons with disabilities is growing thrugh enhancing auditory experiences for those with hearing disabilities. Smart hearing aids powered by machine learning algorithms can filter background noise, amplify relevant sounds, and adapt to the user’s environment. AI-enabled transcription services and real-time captioning have made educational institutions, entertainment platforms, and workplaces far more inclusive.
Mobility and Independence: Smart Navigation Systems

Mobility challenges can significantly limit independence, but AI-powered navigation and robotics are breaking these barriers. Smart wheelchairs equipped with sensors and obstacle detection systems help users move safely through complex environments. Autonomous mobility devices, including robotic guides and AI-powered exoskeletons, are providing new levels of autonomy to people with limited mobility.
AI also plays a critical role in creating intelligent navigation systems for the visually impaired. Tools like Microsoft Soundscape use spatial audio cues to describe surroundings, helping users orient themselves and navigate unfamiliar areas with confidence. This technology transforms mobility into empowerment, enabling users to explore the world independently.
AI in Education: Personalized Learning for All
Education is one of the most powerful tools for empowerment, and AI in empowering persons with disabilities is itself a way of ensuring that learning becomes more inclusive than ever. Adaptive learning platforms analyze students’ strengths, weaknesses, and learning styles, offering customized lesson plans and pacing. This ensures that learners with cognitive or developmental disabilities receive the support they need to thrive.
AI can also assist educators in identifying learning challenges early. For instance, predictive analytics tools can detect patterns that signal dyslexia, ADHD, or other learning difficulties. By intervening early, teachers can provide targeted support that helps students overcome barriers before they widen.
Text-to-speech and speech-to-text systems are enhancing accessibility in classrooms, while AI-based virtual tutors provide individualized assistance outside traditional settings. In this way, AI doesn’t just level the educational playing field, it redefines it.
Workplace Inclusion: Redefining Employment Opportunities
AI is also transforming employment opportunities for persons with disabilities. Smart recruitment systems now focus on skill-based assessments rather than biased indicators, helping eliminate barriers in hiring processes. Remote work technologies powered by AI-driven automation and virtual collaboration tools enable people to contribute effectively from anywhere.
AI-driven accessibility features like screen readers, predictive typing, and adaptive user interfaces make professional software more inclusive. Companies that integrate these technologies not only improve productivity but also foster diversity and innovation within their workforce.
Furthermore, AI in empowering persons with disabilities leads to the fact of opening entirely new job categories. From labeling training data to supervising AI behavior, persons with disabilities are finding meaningful work in the very industry that is empowering them. This symbiotic relationship between inclusion and innovation is redefining what the future of work looks like.
AI in Healthcare and Rehabilitation
Healthcare is one of the most vital areas where AI is transforming disability support. Machine learning algorithms can analyze medical data to predict potential complications, helping doctors create better rehabilitation plans. AI-powered prosthetics are designed to respond to neural signals, making them more natural and responsive.
Rehabilitation robots assist in physical therapy by tracking progress and adjusting difficulty levels based on the patient’s condition. Similarly, AI-enabled mental health applications provide cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) support and monitor emotional well-being, ensuring continuous and personalized care.
The integration of wearable sensors, AI analytics, and IoT devices allows real-time monitoring of vital signs, alerting caregivers or medical professionals when necessary. This continuous support ecosystem significantly improves quality of life and promotes independence.
Social and Emotional Empowerment
Beyond the practical aspects of communication, mobility, and work, AI also plays an essential role in emotional well-being. Virtual companions and social AI platforms offer companionship and support, especially for individuals dealing with isolation or limited social interaction. AI in empowering persons with disabilities is a system, where the design is set to recognize emotions and respond empathetically, can help reduce loneliness and foster a sense of belonging.
AI’s role in storytelling and creative expression is equally important. Platforms that convert visual art into tactile formats or use text-to-audio narrations allow people with disabilities to experience and create art in new ways. Inclusion in culture and creativity builds confidence, representation, and empowerment beyond technology.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI holds enormous potential, it also raises critical ethical questions. Accessibility solutions must be designed with inclusivity and privacy in mind. Data collection for AI models should respect consent and security standards, particularly when handling sensitive health or behavioral information.
There is also a need for continuous improvement in AI bias mitigation. If trained on non-diverse datasets, AI models may inadvertently exclude or misinterpret disability-related contexts. Collaboration between technologists, disability advocates, and policymakers is crucial to ensure that AI tools truly serve their intended users.
The Future of AI Empowerment
The future of AI in disability empowerment lies in integration, personalization, and empathy. As AI continues to advance, technologies will become even more intuitive, adapting dynamically to the unique needs of each individual. With developments in brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), emotion recognition, and autonomous assistance, the line between human and machine collaboration will continue to blur—in the best possible way.
The goal is not to replace human support but to enhance it. AI will continue to complement caregivers, educators, and employers, making inclusion a universal reality rather than an aspiration.
Conclusion
AI is not just about algorithms and data; it is about possibilities. It is about giving every individual the tools to live with dignity, independence, and confidence. From communication and education to healthcare and employment, AI is transforming the lives of people with disabilities, empowering them to participate fully in society.
As we look toward a future powered by innovation, the most meaningful progress will be measured not by how intelligent our machines become, but by how much they help humanity thrive together.